Someone recently asked about the Python sum function at the New York Python user group meeting. In this tutorial, I will explain the sum() function in Python with some examples. As a Python developer you should know about this function.
The sum() function in Python is a built-in function that adds up all the numerical values in an iterable, such as a list, tuple, or set. The syntax is sum(iterable, start), where iterable is the required parameter containing the numbers to be summed, and start is an optional parameter that specifies the starting value, defaulting to 0. For example, sum([1000, 1500, 2000]) will return 4500, efficiently calculating the total of the numbers in the list.
What is the Sum() Function in Python?
The sum() function in Python is a built-in function that adds up all the numerical values in an iterable, such as a list or tuple. This function is incredibly useful for performing quick and efficient summation operations without writing extensive code.
Syntax of the Sum() Function
The syntax of the sum() function is:
sum(iterable, start)iterable: This is the required parameter. It can be any iterable, such as a list, tuple, or set, containing numerical values.start: This is an optional parameter. It specifies the starting value to which the sum of the iterable is added. By default, it is set to 0.
Check out MAX Function in Python
Examples of Using the Sum() Function in Python
Let me show you some practical examples to understand how the sum() function works.
Example 1: Sum a List of Numbers
Suppose we have a list of numbers representing the sales figures for a week in New York City.
sales_figures = [1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000, 3500, 4000]
total_sales = sum(sales_figures)
print("Total Sales for the Week: $", total_sales)In this example, the sum() function calculates the total sales for the week, which is $17500.
I executed the above Python code using VS code, and you can see the exact output in the screenshot below:

Example 2: Sum with a Starting Value
Let’s say we want to add a bonus amount to the total sales. We can use the start parameter to include this bonus.
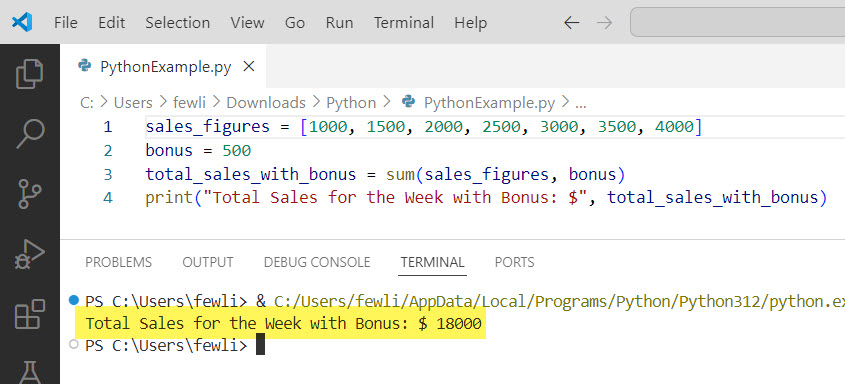
sales_figures = [1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000, 3500, 4000]
bonus = 500
total_sales_with_bonus = sum(sales_figures, bonus)
print("Total Sales for the Week with Bonus: $", total_sales_with_bonus)Here, the sum() function adds the bonus of $500 to the total sales, resulting in $18000.
You can see the exact output in the screenshot below:
Check out Strip Function in Python
Example 3: Sum a Tuple of Numbers
The sum() function can also handle tuples. Consider a tuple of monthly expenses for a family in Los Angeles.
monthly_expenses = (1200, 1300, 1100, 1500, 1700)
total_expenses = sum(monthly_expenses)
print("Total Monthly Expenses: $", total_expenses)This example calculates the total monthly expenses, which is $6800.
Example 4: Sum with Different Data Types
You can also use the sum() function with different data types, as long as they are numerical. Here’s an example with a set of utility bills in Chicago.
utility_bills = {200, 300, 150, 100, 250}
total_utility_bills = sum(utility_bills)
print("Total Utility Bills: $", total_utility_bills)In this case, the sum() function calculates the total utility bills, which is $1000.
After I executed the above Python code using VS code, you can see the exact output in the screenshot below:

Conclusion
The sum() function in Python helps to quickly sum up numerical values in an iterable. Whether you are working with lists, tuples, or sets, this function simplifies adding numbers together. In this tutorial, I explained how to work with the sum() function in Python with a few real examples.
You may also like:

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…