Recently, I was working in a while loop in Python and got a scenario to stop the loop prematurely based on specific conditions. I researched it and found our different methods. In this tutorial, I will explain different methods to stop a while loop in Python with some examples.
To stop a while loop in Python, you can use the break statement. When encountered within a loop, the break statement immediately terminates the loop and transfers the program control to the next statement after the loop. This allows you to stop the loop prematurely based on specific conditions or requirements.
The break Statement
The best way to stop a while loop in Python is by using the break statement. When encountered within a loop, the break statement immediately terminates the loop and transfers the program control to the next statement after the loop.
Here’s an example that demonstrates the usage of break to stop a while loop:
# Example: Ticket Reservation System
tickets_available = 100
while tickets_available > 0:
num_tickets = int(input("Enter the number of tickets you want to reserve: "))
if num_tickets <= tickets_available:
tickets_available -= num_tickets
print(f"Reservation successful! {num_tickets} tickets reserved.")
else:
print("Sorry, not enough tickets available.")
break
print("Ticket reservation system closed.")In this example, we have a ticket reservation system where users can reserve tickets until there are no more tickets available.
The while loop continues as long as tickets_available is greater than 0. Inside the loop, we prompt the user to enter the number of tickets they want to reserve.
If the requested number of tickets is available, we update the tickets_available count and display a success message. However, if the requested tickets exceed the available count, we print an error message and use the break statement to stop the loop immediately.
Here is the output you can see in the screenshot below:
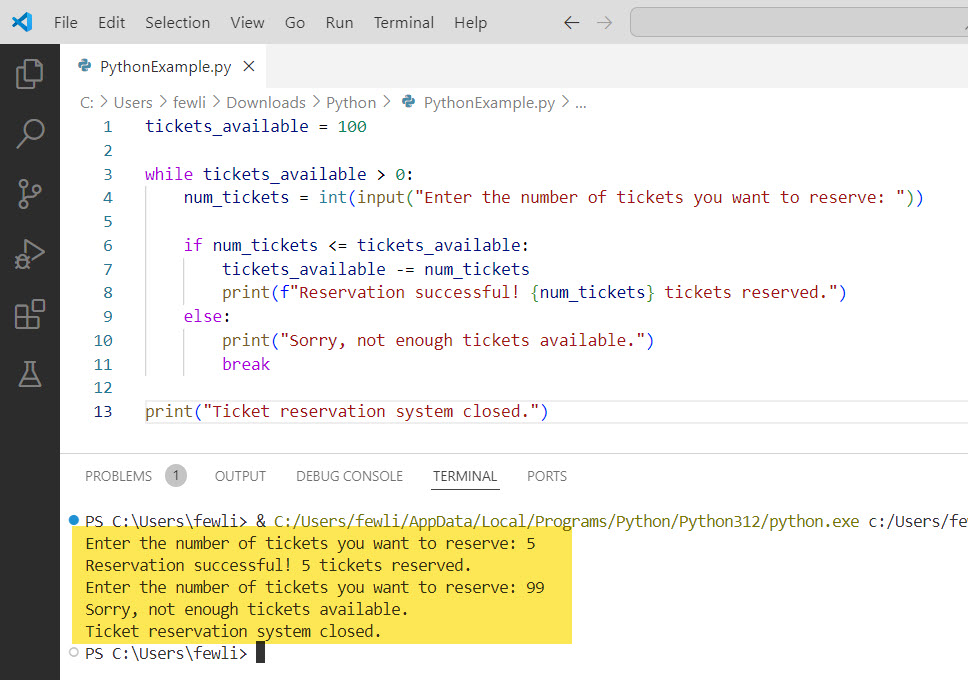
Check out Python While Loop Break and Continue
The continue Statement
Another way to control the flow of a while loop is by using the continue statement. When encountered within a loop, the continue statement skips the rest of the current iteration and moves the program control to the next iteration of the loop.
Here’s an example that explains the usage of continue in a while loop:
# Example: Discount Eligibility Checker
age = 0
while age < 100:
age = int(input("Enter your age: "))
if age < 18:
print("Sorry, you are not eligible for the discount.")
continue
elif age >= 65:
print("Congratulations! You are eligible for a 20% senior citizen discount.")
else:
print("Congratulations! You are eligible for a 10% discount.")
print("Thank you for using the discount eligibility checker!")In this example, we have a discount eligibility checker that determines the discount based on the user’s age.
The while loop continues until the user enters an age greater than or equal to 100. Inside the loop, we prompt the user to enter their age.
If the age is less than 18, we print a message indicating that the user is not eligible for the discount and use the continue statement to skip the rest of the current iteration and move to the next one.
If the age is greater than or equal to 65, we print a message indicating a 20% senior citizen discount. Otherwise, we print a message indicating a 10% discount.
Here is an output you can see in the screenshot below:
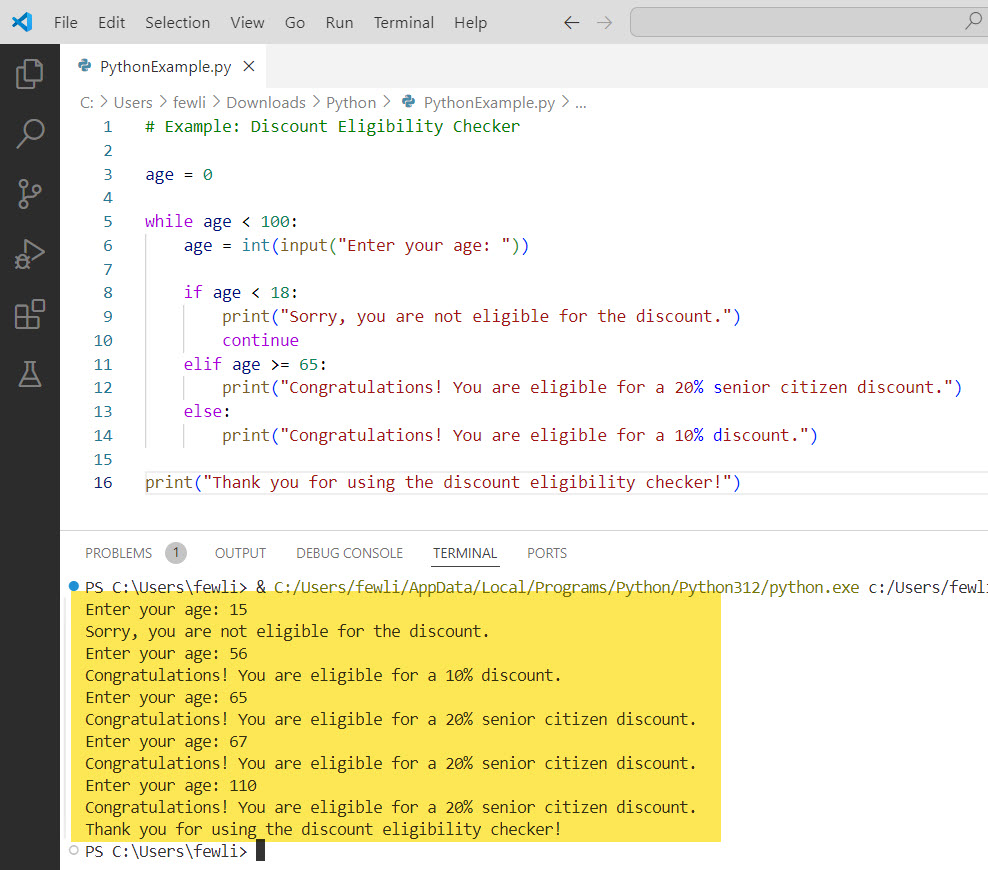
Using Flags or Sentinel Values
Another approach to stop a while loop is by using flags or sentinel values. A flag is a boolean variable that can be set to True or False to control the loop execution. A sentinel value is a specific value that indicates the end of the loop.
Here’s an example that explains the usage of a flag to stop a while loop:
# Example: Password Validator
valid_password = False
while not valid_password:
password = input("Enter a password (minimum 8 characters): ")
if len(password) >= 8:
valid_password = True
print("Password accepted!")
else:
print("Password too short. Please try again.")
print("Password validation complete.")In this example, we have a password validator that prompts the user to enter a password until a valid password (minimum 8 characters) is provided. We use a flag variable valid_password initialized to False.
The while loop continues as long as valid_password is False. Inside the loop, we prompt the user to enter a password. If the length of the password is greater than or equal to 8, we set valid_password to True and print a success message. Otherwise, we print an error message and the loop continues.
Here is the output you can see in the screenshot below:
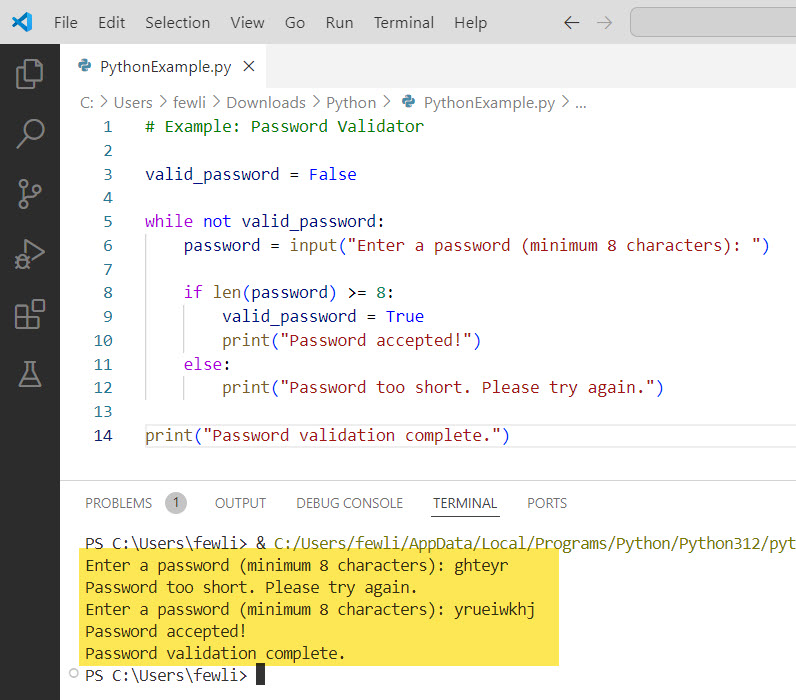
Conclusion
In this tutorial, I have explained different methods to stop a while loop in Python. We covered the usage of the break statement to immediately terminate the loop, the continue statement to skip the current iteration and move to the next one, and the concept of using flags or sentinel values to control the loop execution.
Also, I tried my best to provide you with the best examples and code explanations.

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…