In this tutorial, I will explain how to use the reduce() function in Python, including its syntax and some real examples.
The reduce() function in Python, found in the functools module, allows you to apply a specified function cumulatively to the items of an iterable, effectively reducing it to a single cumulative value. For instance, to sum a list of numbers, you can use reduce(lambda x, y: x + y, [1500, 2000, 3000, 2500, 4000]), which will return 13000.
What is the reduce Function in Python?
The reduce function is a part of Python’s functools module. It is used to apply a specific function cumulatively to the items of an iterable (like a list), reducing the iterable to a single cumulative value. Essentially, it performs a repetitive operation over the pairs of the iterable.
Why Use the reduce() Function?
Using the reduce function can simplify your code when you need to perform cumulative operations on a list or any other iterable. It can make your code more readable and concise, especially for operations like summing numbers, finding the maximum value, or concatenating strings.
Syntax of the reduce Function
The syntax of the reduce function is:
from functools import reduce
reduce(function, iterable[, initializer])- function: A function that takes two arguments and returns a single value.
- iterable: The iterable (e.g., list, tuple) whose elements are to be reduced.
- initializer (optional): A value to start the accumulation with.
Check out join() Function in Python
Examples of Using the Python reduce() Function
Let me show you some practical examples to understand how the reduce function works in Python.
Example 1: Sum a List of Numbers
Suppose we have a list of sales figures from different cities in the USA and want to calculate the total sales. We can use the Python code below.
from functools import reduce
sales = [1500, 2000, 3000, 2500, 4000]
total_sales = reduce(lambda x, y: x + y, sales)
print(total_sales) # Output: 13000In this example, reduce takes a lambda function that adds two numbers and applies it cumulatively to the list of sales figures.
Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:

Check out append() Function in Python
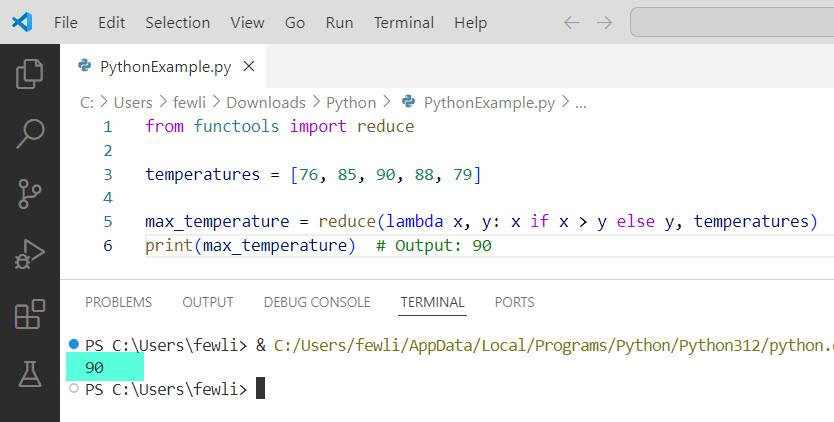
Example 2: Find the Maximum Value
Let’s say we have a list of temperatures recorded in various cities across the USA, and we want to find the highest temperature.
Here is the complete Python code.
from functools import reduce
temperatures = [76, 85, 90, 88, 79]
max_temperature = reduce(lambda x, y: x if x > y else y, temperatures)
print(max_temperature) # Output: 90Here, reduce helps us find the maximum temperature by comparing each pair of temperatures.
Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:
Check out ord() function in Python
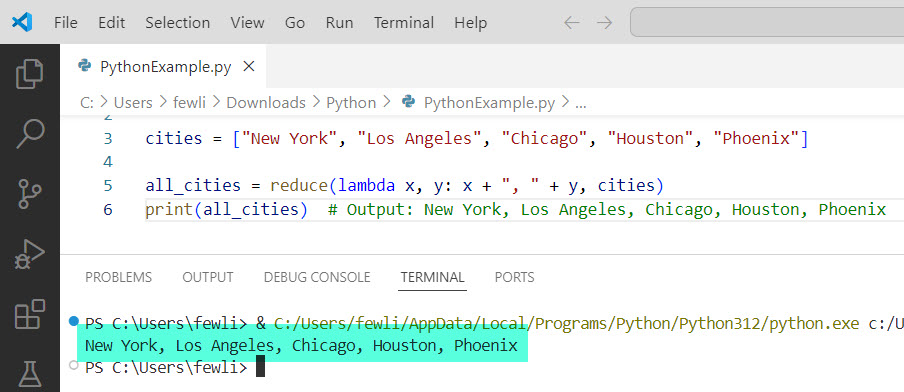
Example 3: Concatenate Strings
Imagine we have a list of city names, and we want to create a single string with all the names concatenated; you can use the below Python code.
from functools import reduce
cities = ["New York", "Los Angeles", "Chicago", "Houston", "Phoenix"]
all_cities = reduce(lambda x, y: x + ", " + y, cities)
print(all_cities) # Output: New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston, PhoenixIn this case, reduce concatenates all the city names into a single string.
Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:
Conclusion
The reduce function in Python helps perform cumulative operations on iterables. In this tutorial, I explained the reduce function syntax and how to apply it with practical examples.
You may also like the following tutorials:
- POP() Function in Python
- Range Function in Python
- Square Root Function in Python
- Log() Function in Python

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…