In today’s tutorial, I will focus only on using break and continue in a Python while loop. I will show you how to use break and continue in Python while loops.
A while loop in Python repeatedly executes a block of code as long as a given condition is true. Here’s a simple example:
count = 0
while count < 5:
print("Count is:", count)
count += 1This loop will print the value of count from 0 to 4. But what if we want to stop the loop prematurely or skip certain iterations? This is where break and continue come into play.
The Break Statement in While Loop
The break statement in the while loop is used to exit the loop immediately, regardless of the loop’s condition. This can be useful in various scenarios, such as when searching for an item in a list and wanting to stop once you’ve found it.
Example: Finding a Specific Item in a List
Suppose you have a list of products and want to find a specific one. Once you find the product, you want to stop the search.
products = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date", "elderberry"]
search_item = "cherry"
index = 0
while index < len(products):
if products[index] == search_item:
print(f"Found {search_item} at index {index}")
break
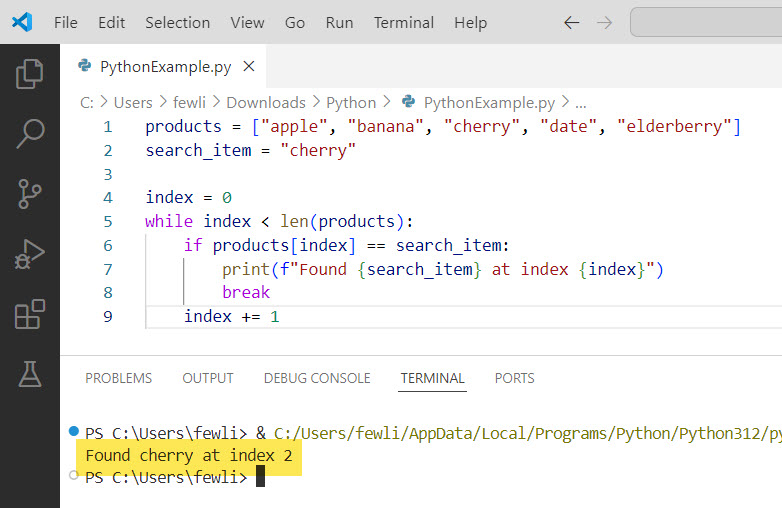
index += 1In this example, the loop will terminate as soon as it finds “cherry,” thanks to the break statement.
I executed the above Python code, and you can see the output in the screenshot below:
The Continue Statement in While Loop
The continue statement in the while loop is used to skip the rest of the code inside the loop for the current iteration and move to the next iteration. This is useful when you want to skip certain conditions but continue looping.
Example: Skipping Even Numbers
Suppose you want to print only odd numbers from 1 to 10. You can use the continue statement to skip even numbers.
number = 0
while number < 10:
number += 1
if number % 2 == 0:
continue
print("Odd number:", number)In this example, the continue statement skips the even numbers and only prints the odd ones.
Here is the output in the screenshot below:

Check out How to Stop a While Loop in Python
Combining Break and Continue in While Loop
You can also use break and continue together in a while loop to create more complex control flows.
Example: Processing a List of Orders
Consider a scenario where you have a list of orders, and you want to process each order unless it’s flagged as fraudulent. If a fraudulent order is found, you want to stop processing entirely.
orders = [
{"id": 1, "amount": 100, "fraudulent": False},
{"id": 2, "amount": 200, "fraudulent": False},
{"id": 3, "amount": 150, "fraudulent": True},
{"id": 4, "amount": 300, "fraudulent": False}
]
index = 0
while index < len(orders):
order = orders[index]
if order["fraudulent"]:
print(f"Fraudulent order detected: {order['id']}. Stopping processing.")
break
if order["amount"] < 150:
print(f"Skipping small order: {order['id']}")
index += 1
continue
print(f"Processing order: {order['id']}")
index += 1In this example, the loop processes each order, skips orders with amounts less than 150, and stops entirely if a fraudulent order is detected.
Python While Loop Break and Continue Example
Now, let me show you a few examples of using Python while loop break and continue.
I will show you an example of data validation in Python.
Suppose you’re building a user registration system where users input their age. You can use a while loop with break and continue to validate the input:
while True:
age = input("Enter your age: ")
if not age.isdigit():
print("Invalid input. Please enter a numeric value.")
continue
age = int(age)
if age < 0:
print("Age cannot be negative.")
continue
if age >= 18:
print("Registration successful!")
break
else:
print("You must be at least 18 years old to register.")
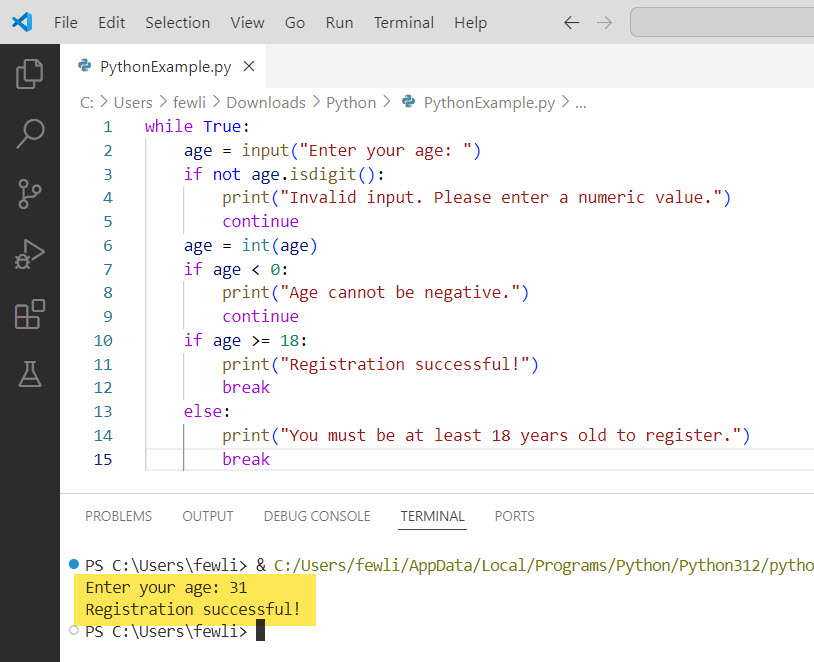
breakIn this example, we use a while loop to repeatedly prompt the user for their age until a valid input is provided. The continue statement is used to handle invalid inputs (non-numeric values or negative numbers) and prompt the user again. The break statement is used to exit the loop when a valid age is entered, either allowing registration for users 18 and older or denying registration for those under 18.
You can see the output in the screenshot below:
Conclusion
The break and continue statements are essential tools for controlling the flow of while loops in Python. They allow you to exit loops prematurely or skip specific iterations, making your code more efficient and readable. In this tutorial, I have explained how to use the break and continue statements in a while loop in Python with a few examples.

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…