Today, I will show a very important topic related to functions in Python: how to pass a function as an argument in Python with examples. As a Python developer, you should know this.
Passing a function as an argument in Python is often used for implementing callbacks, which are functions executed after a specific event or task is completed. For example, you can pass success and failure callback functions to a data processing function. Depending on whether the operation is successful or encounters an error, the corresponding callback function is invoked to handle the result or error, making your code more modular and responsive. For instance:
def on_success(result):
print(f"Success: {result}")
def on_failure(error):
print(f"Error: {error}")
def process_data(data, success_callback, failure_callback):
try:
result = data / 2
success_callback(result)
except Exception as e:
failure_callback(e)
process_data(10, on_success, on_failure)Why Pass a Function as an Argument in Python?
Passing a function as an argument allows you to create higher-order functions. These are functions that operate on other functions, either by taking them as arguments or by returning them. This can be incredibly useful for scenarios like callbacks, event handling, or simply making your code more dynamic and flexible.
Syntax
In Python, functions are first-class citizens. You can pass them around as arguments to other functions, just like any other object (e.g., strings, integers, lists). Here’s a basic example to illustrate this:
def greet(name):
return f"Hello, {name}!"
def execute_function(func, value):
return func(value)
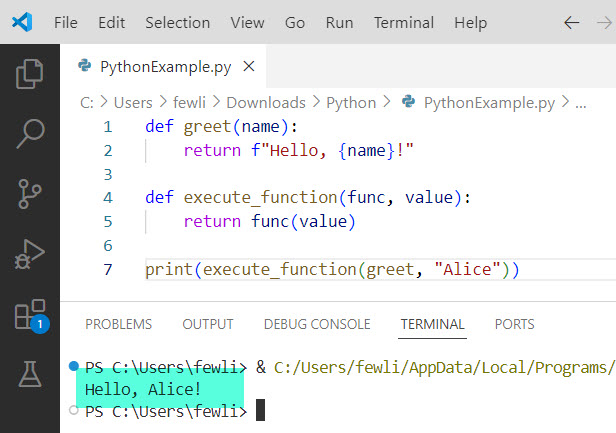
print(execute_function(greet, "Alice"))In this example, greet is passed as an argument to execute_function. The execute_function then calls greet with the provided value.
You can see the output in the screenshot below:
Check out Return Multiple Values from a Function in Python
Pass a Function as an Argument in Python
Now, let me show you different methods to pass a function as an argument in Python.
1. Using Functions as Callbacks
One common use case for passing functions as arguments is in callback functions in Python. Callbacks are often used for event handling or asynchronous programming.
Here is an example and the complete Python code.
def on_success(result):
print(f"Success: {result}")
def on_failure(error):
print(f"Error: {error}")
def process_data(data, success_callback, failure_callback):
try:
# Simulate processing data
result = data / 2
success_callback(result)
except Exception as e:
failure_callback(e)
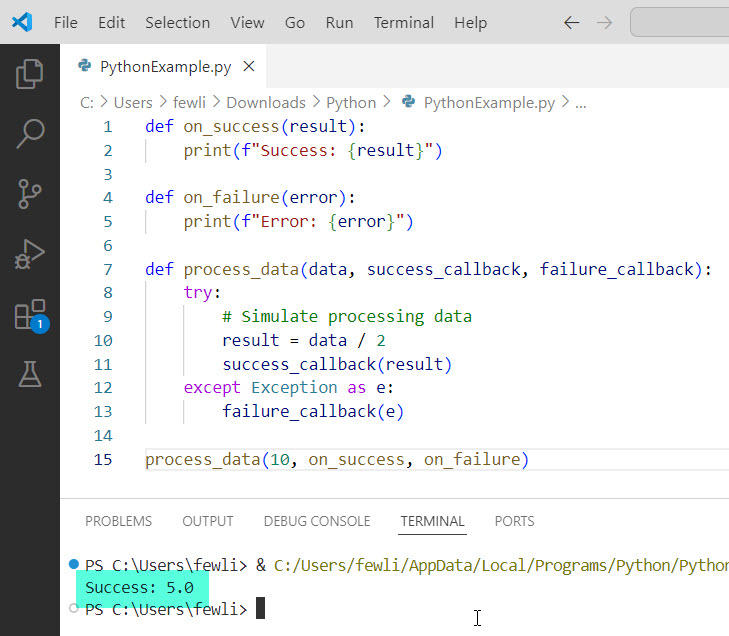
process_data(10, on_success, on_failure)Here, on_success and on_failure are passed as callbacks to process_data. Depending on whether the data processing is successful or not, the respective callback is invoked.
Here is the output in the screenshot below:
2. Higher-Order Functions
Higher-order functions either take other functions as parameters or return them as results. This is a powerful feature that can simplify complex operations.
Here is an example.
def add(x, y):
return x + y
def subtract(x, y):
return x - y
def apply_operation(operation, a, b):
return operation(a, b)
print(apply_operation(add, 5, 3)) # Output: 8
print(apply_operation(subtract, 5, 3)) # Output: 2In this scenario, apply_operation is a higher-order function that takes another function (add or subtract) as an argument and applies it to the given numbers.
Check out Python Function Naming Conventions
3. Using *args and **kwargs
You can also pass functions using *args and **kwargs for more dynamic and flexible function calls. Here is another example of how to pass a function as an argument in Python.
def multiply(x, y):
return x * y
def apply_operations(func, *args):
return func(*args)
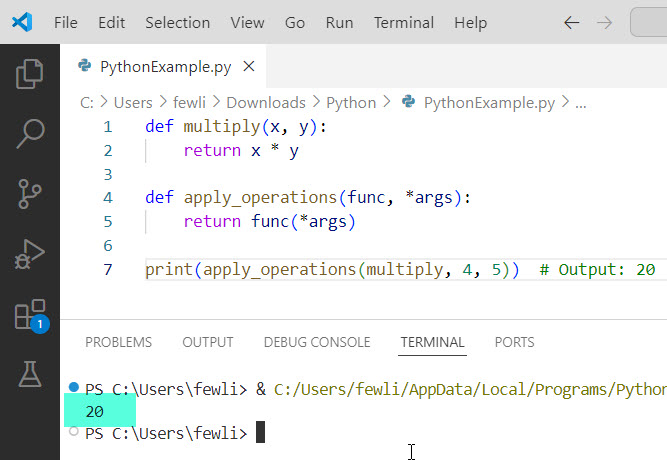
print(apply_operations(multiply, 4, 5)) # Output: 20This method allows you to pass various arguments to the function, making it highly versatile.
Here is the output in the screenshot below:
4. Functional Programming with map, filter, and reduce
Python’s built-in functions like map, filter, and reduce are excellent examples of higher-order functions. Here is another example of passing a function as an argument in Python.
def square(x):
return x * x
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = list(map(square, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, map takes the square function and applies it to each item in the numbers list.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, I explained how to pass functions an arguments in Python using different methods and various examples. If you still have questions, then leave a comment below.
You may also like the following tutorials:
- How to Call a Function by String in Python?
- Call a Function from Another File in Python
- Python Function Default Arguments

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…