Recently, one of my team members was asking to know how to make a variable global in Python. I suggested a complete solution. In this tutorial, I will show you how to make a variable global in Python using various methods and examples. Variables can either be local or global. Local variables are defined within a function and are accessible only within that function, while global variables are accessible throughout the entire Python code.
To make a variable global in Python, declare it outside any function so it can be accessed throughout the entire program. For example:
# Global variable
country_name = "United States of America"
def print_country():
print(f"The country is {country_name}")
print_country()Here, country_name is a global variable, accessible within the print_country function without any special keywords.
What is a Global Variable in Python?
A global variable in Python is one that is declared outside of any function and is accessible throughout the entire program. It can be used and modified by any function within the script.
Create a Global Variable in Python
To create a global variable in Python, you simply declare it outside of any function. Here’s an example:
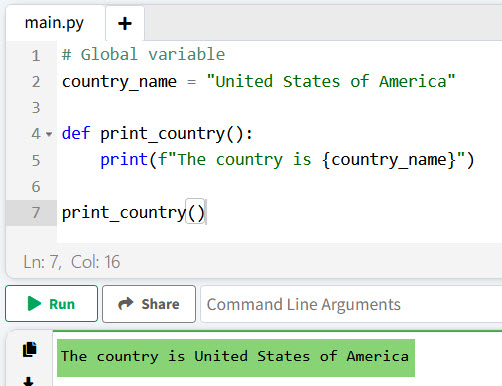
# Global variable
country_name = "United States of America"
def print_country():
print(f"The country is {country_name}")
print_country()In this example, country_name is a global variable. The function print_country can access and print it without any issues.
I executed the above Python code, and you can see the output in the screenshot below:
Check out Check if a Variable Exists in Python
Modify a Global Variable
To modify a global variable inside a function, you need to use the global keyword in Python. Without this keyword, Python treats the variable as a local variable within the function scope. Here’s an example:
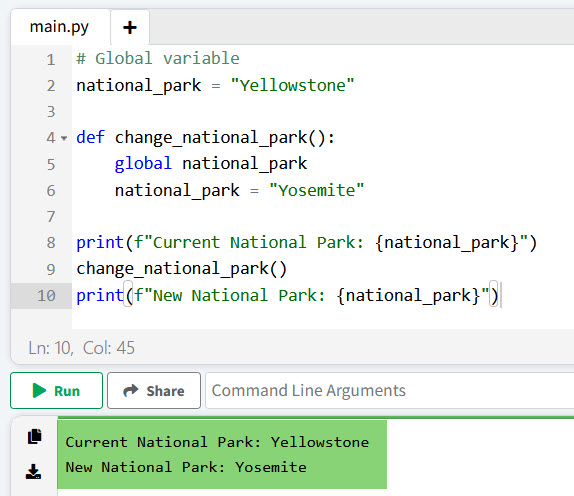
# Global variable
national_park = "Yellowstone"
def change_national_park():
global national_park
national_park = "Yosemite"
print(f"Current National Park: {national_park}")
change_national_park()
print(f"New National Park: {national_park}")In this example, national_park is a global variable that is modified within the change_national_park function using the global keyword.
Here is the output in the screenshot below; after I executed the above Python code.
Access a Global Variable in Python
In Python, you can access a global variable from within any function without using the global keyword. Here’s an example:
# Global variable
state_capital = "Washington, D.C."
def print_capital():
print(f"The capital of the USA is {state_capital}")
print_capital()In this example, state_capital is a global variable, and the print_capital function can access it directly.
Check out Print String and Variable in Python
Using Global Variables in Nested Functions
Global variables can also be accessed and modified in nested functions in Python. Here’s an example:
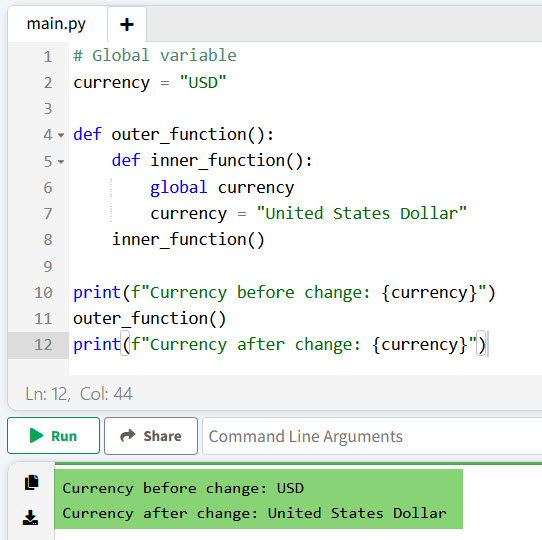
# Global variable
currency = "USD"
def outer_function():
def inner_function():
global currency
currency = "United States Dollar"
inner_function()
print(f"Currency before change: {currency}")
outer_function()
print(f"Currency after change: {currency}")In this example, the inner_function modifies the global variable currency using the global keyword.
When you execute the above Python code, you will also get the exact output, as in the screenshot below.
Change a Global Variable in a Function in Python
I will show you an example here where I wanted to change a global variable in a function in Python.
We’ll use a global variable to store the population and write functions to increase and decrease the population. Here, we will do the following:
- Declare the Global Variable: We’ll start by declaring a global variable outside any function.
- Modify the Global Variable: Inside a function, we’ll use the
globalkeyword to modify the global variable.
Below is the complete code:
# Global variable
population = 500000 # Initial population of the city
def increase_population(amount):
global population # Declare that we want to use the global variable
population += amount
print(f"Population increased by {amount}. New population: {population}")
def decrease_population(amount):
global population # Declare that we want to use the global variable
if population >= amount:
population -= amount
print(f"Population decreased by {amount}. New population: {population}")
else:
print("Population cannot be negative.")
def get_population():
return population
# Test the functions
print(f"Initial population: {get_population()}")
increase_population(20000)
decrease_population(5000)
decrease_population(600000) # This should trigger the "cannot be negative" message
print(f"Final population: {get_population()}")Once you execute the above Python code, you will see the output like the below:
Initial population: 500000
Population increased by 20000. New population: 520000
Population decreased by 5000. New population: 515000
Population cannot be negative.
Final population: 515000Here is the code explanation for you to understand.
- Initial Population: We start with a global variable
populationset to500000. - Increase Population: The
increase_populationfunction takes anamountparameter and uses theglobalkeyword to modify the globalpopulationvariable. It adds the given amount to the population and prints the new value. - Decrease Population: Similarly, the
decrease_populationfunction uses theglobalkeyword to modify the globalpopulationvariable. It subtracts the given amount from the population but includes a check to ensure the population doesn’t go negative. - Get Population: The
get_populationfunction simply returns the current value of the globalpopulationvariable.
By using the global keyword in the increase_population and decrease_population functions, we ensure that the global population variable is modified directly, rather than creating a new local variable with the same name.
This is how to modify a global variable in a function in Python.
Check out How to Check if a Variable is Global in Python?
Best Practices for Using Python Global Variables
Here are some best practices you should follow while using global variables in Python.
- Limit the Use of Global Variables: Use global variables only when absolutely necessary.
- Use Clear and Descriptive Names: Give your global variables clear and descriptive names to avoid confusion.
- Document Your Code: Make sure to document your code to explain why a global variable is used.
- Avoid Global Variables in Large Projects: In large projects, try to avoid using global variables as they can make debugging and testing more difficult.
Conclusion
Global variables in Python can be powerful when used correctly. They allow you to share data across multiple functions and parts of your program. However, it’s important to use them correctly to maintain the readability and maintainability of your code.
By understanding the scope of variables and using the global keyword appropriately, you can effectively manage and manipulate global variables in your Python programs.
In this tutorial, I explained how to make a variable global in Python using the global keyword with examples.
You may also like the following tutorial:
- How to Use Static Variables in Python?
- Create Dynamic Variables in Python
- How to Check if a Global Variable is Initialized in Python?

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…