In this tutorial, I explained how to use the log() function in Python and its syntax and examples.
What is the Log Function in Python?
The log function in Python is used to calculate the logarithm of a given number. Python provides several built-in logarithmic functions under the math module, allowing us to compute logs with ease. Logarithms are essential in various fields, such as mathematics, data science, and engineering.
Here are some use cases of the Python log function.
- Logarithms are commonly used in data analysis to transform skewed data into a more normal distribution. This can be particularly useful when dealing with financial data or population growth rates.
- Logarithms are often used in machine learning algorithms such as logistic regression and neural networks. They help scale features and deal with large data sets.
- In scientific computing, logarithms are used to solve equations involving exponential growth or decay, such as radioactive decay or population dynamics.
Check out Len() Function in Python
Syntax of Log Function in Python
Python’s math module offers several logarithmic functions, including:
math.log(x, base)math.log10(x)math.log2(x)
Import the Math Module
Before using any log function, you need to import the Python math module:
import mathSyntax
Here’s the general syntax for the log function in Python:
math.log(x, base)x: The number for which you want to calculate the logarithm.base: The base of the logarithm. If not specified, the natural logarithm (basee) is calculated.
Read reduce() Function in Python
Examples of Log() Function in Python
Let me show you some examples of how the log function works in Python.
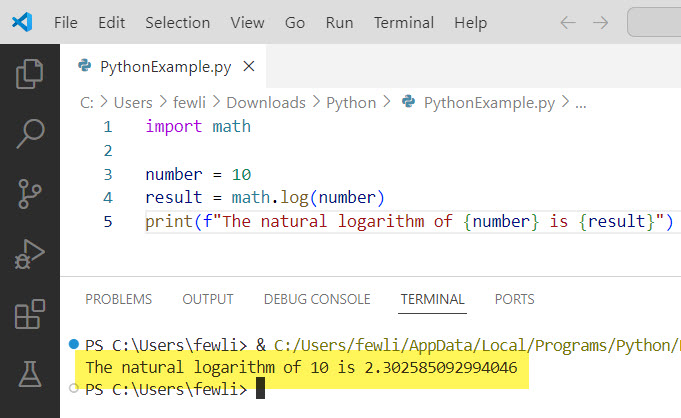
Example 1: Natural Logarithm
The natural logarithm uses the base e (approximately 2.71828). Here’s how you can calculate it:
import math
number = 10
result = math.log(number)
print(f"The natural logarithm of {number} is {result}")I executed the above Python code using VS code, and you can see the exact output in the screenshot below:
Example 2: Logarithm with Base 10
For a base 10 logarithm, you can use math.log10() in Python. Here is an example.
import math
number = 100
result = math.log10(number)
print(f"The base 10 logarithm of {number} is {result}")Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:

Read join() Function in Python
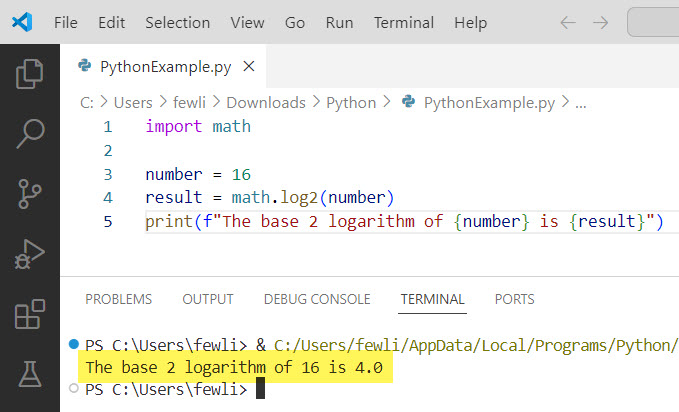
Example 3: Logarithm with Base 2
For a base 2 logarithm, you can use math.log2() function. Here is the Python code.
import math
number = 16
result = math.log2(number)
print(f"The base 2 logarithm of {number} is {result}")Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:
Example 4: Custom Base Logarithm
You can also specify a custom base:
import math
number = 81
base = 3
result = math.log(number, base)
print(f"The logarithm of {number} with base {base} is {result}")Conclusion
In this tutorial, I explained how to use the log function in Python for various applications in data science, engineering, or scientific research. I hope this tutorial has provided you with a clear understanding of the log function in Python.
You may also like the following tutorials:

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…