In today’s tutorial, I will explain how to work with Python’s len() function with some examples. You will get to know how to use len() to determine the length of various data types in Python.
The len() function in Python is a built-in function that returns the number of items in an object, such as a string, list, tuple, dictionary, or set. For example, when used with a string, len() returns the number of characters in the string. Here’s a quick example: if you have city_name = "San Francisco", len(city_name) will return 13, which is the total number of characters in the string.
What is the len() Function in Python?
The len() function is a built-in Python function that returns the number of items in an object. This object can be a string, list, tuple, dictionary, or any other iterable.
Syntax of len()
The syntax of the len() function is:
len(object)Here, object refers to the item whose length you want to determine. The function returns an integer representing the number of elements in the object.
Check out reduce() Function in Python
Using Python len() Function with Different Data Types
Now. let me show you how to use Python len() function with different data types.
1. Strings
The len() function can be used to find the length of a string, which is the number of characters in the string. Here is the Python code.
city_name = "San Francisco"
print(len(city_name)) # Output: 13I executed the above code and you can see the exact output in the screenshot below:

2. Lists
For lists, len() returns the number of items in the list in Python. Here is an example.
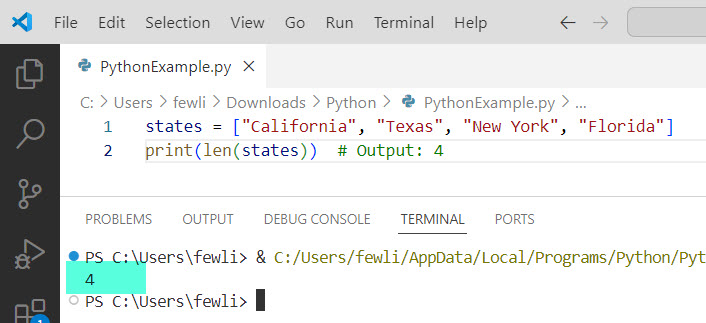
states = ["California", "Texas", "New York", "Florida"]
print(len(states)) # Output: 4Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:
3. Tuples
Tuples, like lists, are collections of items. The len() function can be used to find out how many items are in a tuple. Here is the Python code.
coordinates = (37.7749, -122.4194)
print(len(coordinates)) # Output: 2Check out join() Function in Python
4. Dictionaries
When used with dictionaries, len() returns the number of key-value pairs. Here is the Python code to find the length of a dictionary.
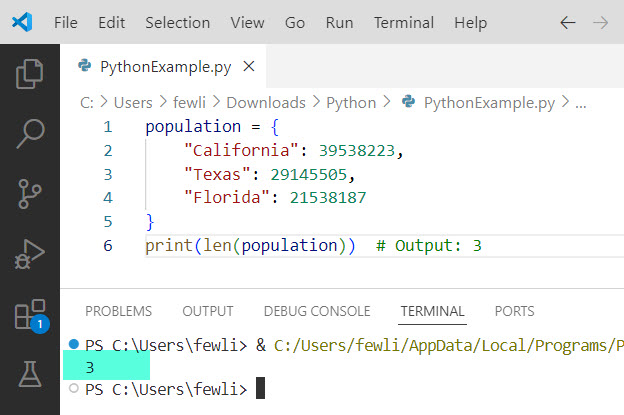
population = {
"California": 39538223,
"Texas": 29145505,
"Florida": 21538187
}
print(len(population)) # Output: 3Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:
5. Sets
Sets are collections of unique items. The len() function can also be used with sets to determine the number of elements. Here is an example.
unique_states = {"California", "Texas", "New York", "Florida", "Texas"}
print(len(unique_states)) # Output: 4Check out append() Function in Python
Len() Function Examples
Now, let me show you two real examples of len() function in Python programming.
Example 1: Check the Length of User Input
You can use len() to validate user input, such as ensuring a username meets a minimum length requirement.
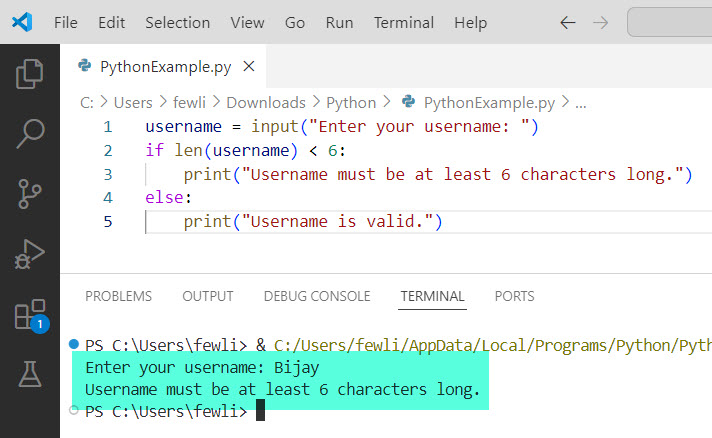
username = input("Enter your username: ")
if len(username) < 6:
print("Username must be at least 6 characters long.")
else:
print("Username is valid.")Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:
Example 2: Count Items in a Shopping List
Suppose you have a shopping list and want to know how many items are on it.
shopping_list = ["apples", "bananas", "oranges", "milk"]
print(f"You have {len(shopping_list)} items in your shopping list.")Common Mistakes to Avoid While using Len() Function
- Using
len()on Non-Iterable Objects: Thelen()function only works with iterable objects. Using it on an integer or a non-iterable object will result in aTypeError.
number = 100
print(len(number)) # This will raise a TypeError- Confusing Length with Index: Remember that
len()returns the number of items, not the index of the last item. For example, in a list with 4 items,len()will return 4, but the last item’s index is 3.
Conclusion
The len() function in Python programming returns the number of items in an object. Whether you’re working with strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, or sets, len() helps you quickly determine the size of your data structures. I hope now you got to know how to use the Python len() function with examples.
You may also like the following tutorials:

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…