In today’s tutorial, I will explain the join() function in Python with examples, including its syntax and usage.
The join function in Python is a string method used to concatenate a sequence of strings into a single string, with a specified separator placed between each element. The syntax is separator.join(iterable), where separator is the string used to separate the elements and iterable is the sequence of strings you want to join. For example, using “, “.join([“New York”, “Los Angeles”, “Chicago”]) will produce the string “New York, Los Angeles, Chicago”.
What is the join Function in Python?
The join function in Python is a string method that allows you to concatenate a sequence of strings into a single string with a specified separator. This function is particularly useful when you need to combine elements of a list or tuple into a single string.
Syntax of the join Function
The syntax of the Python join function is:
separator.join(iterable)- separator: This is the string that will be used to separate the elements of the iterable.
- iterable: This is the sequence (e.g., list, tuple) of strings that you want to join.
Check out append() Function in Python
How Does the join() Function Work?
The join function works by iterating over the elements of the iterable and concatenating them into a single string, with the specified separator placed between each element. It’s important to note that the elements of the iterable must be strings; otherwise, you’ll encounter a TypeError.
Examples of Using the join() Function
Let me show you some practical examples to understand how the join function works in Python.
Join a List of Strings
Suppose we have a list of city names in the USA, and we want to join them into a single string separated by commas.
Here is the Python code you can write.
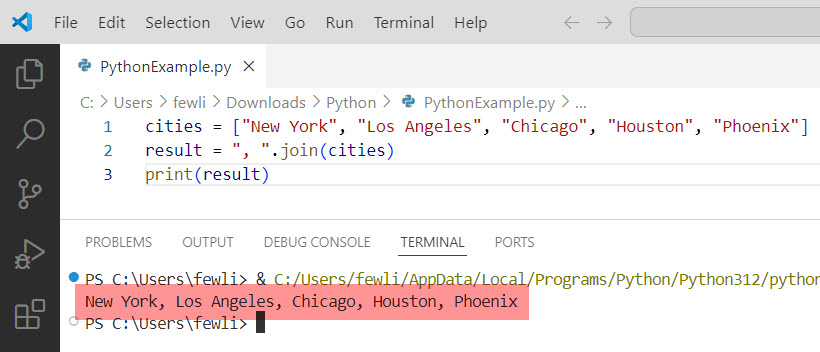
cities = ["New York", "Los Angeles", "Chicago", "Houston", "Phoenix"]
result = ", ".join(cities)
print(result)Output:
New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston, PhoenixI executed the above Python program using VS code, and you can see the output in the screenshot below:
Join with Different Delimiters
You can use different delimiters to join the elements. For instance, if you want to use a hyphen as the separator.
Here is the Python code.
states = ["California", "Texas", "Florida", "New York", "Pennsylvania"]
result = " - ".join(states)
print(result)Output:
California - Texas - Florida - New York - PennsylvaniaHere is the exact output in the screenshot below:

Join with an Empty String
If you want to concatenate the elements without any separator in Python, you can use an empty string as the separator.
Here is the Python code and the example.
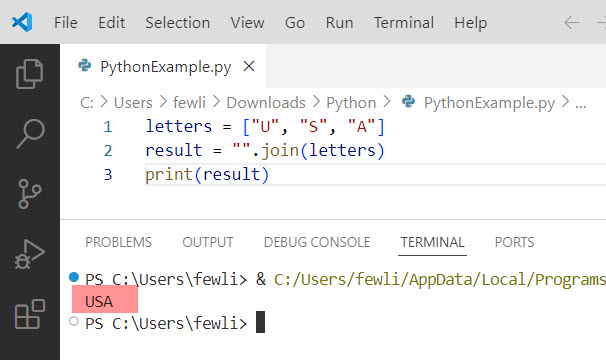
letters = ["U", "S", "A"]
result = "".join(letters)
print(result)Output:
USAHere in the screenshot below you can see the exact output:
Check out ord() function in Python
Best Practices
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when using the join function in Python:
- Ensure Elements are Strings: Always make sure that the elements of the iterable are strings to avoid
TypeError. - Choose Appropriate Separators: Use separators that make the resulting string readable and meaningful.
- Avoid Overuse: While the join() function is powerful, overusing it can make your code harder to read. Use it carefully.
Conclusion
The join function in Python is used for string manipulation. In this tutorial, I explained how to use the join function in Python, including its syntax and usage; you can efficiently concatenate sequences of strings with various separators.
I hope this tutorial has helped you understand the join() function in Python. Please let me know in the comment below if you still have any questions.
You may also like:

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…