One of my team members recently tried to divide a variable in Python. I suggested different methods. In this tutorial, I will show you how to divide a variable in Python using various methods with complete examples.
To divide a variable in Python using the basic method, you simply use the single forward slash (/) operator. This operator performs floating-point division, meaning the result will include any decimal points. For example, result = 10 / 4 will yield 2.5.
1. Basic Division Using the / Operator
The best way to perform division in Python is by using the single forward slash (/) operator. This operator performs floating-point division, which means the result will include any decimal points. Let me show you an example of it.
Example
# Dividing two variables
numerator = 10
denominator = 4
result = numerator / denominator
print(result) # Output: 2.5In this example, dividing 10 by 4 yields 2.5, a floating-point number.
I executed the above Python code, and you can see the output in the screenshot below:

Check out How to Subtract from a Variable in Python?
2. Integer Division Using the // Operator
If you want to perform integer division in Python (also known as floor division), where the result is rounded down to the nearest whole number, you can use the double forward slash (//) operator.
Here is an example to help you understand it better.
Example
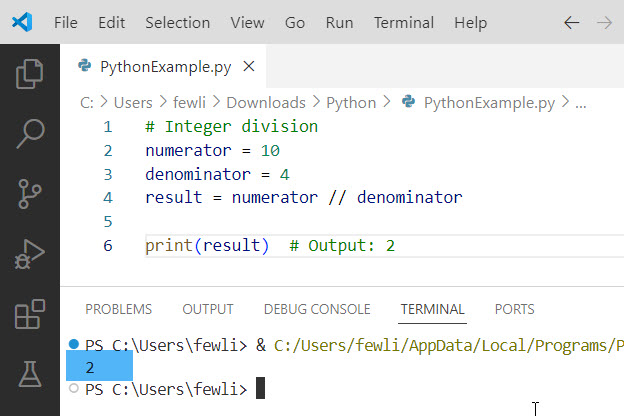
# Integer division
numerator = 10
denominator = 4
result = numerator // denominator
print(result) # Output: 2Here, dividing 10 by 4 using integer division results in 2, discarding the remainder.
Here is the output you can see in the screenshot below:
3. Using the divmod() Function
The divmod() function in Python returns a tuple containing the quotient and the remainder when dividing two numbers. This can be particularly useful for applications that require both values.
Here is an example.
Example
# Using divmod() function
numerator = 10
denominator = 4
quotient, remainder = divmod(numerator, denominator)
print(f"Quotient: {quotient}, Remainder: {remainder}") # Output: Quotient: 2, Remainder: 2In this example, divmod(10, 4) returns (2, 2), where 2 is the quotient and 2 is the remainder.
Read How to Multiply a Variable in Python?
4. Division with Decimal for High Precision
For applications requiring high precision, such as financial calculations, you can use the Decimal class from Python’s decimal module. This is particularly useful for dealing with U.S. currency values.
Let me show you an example.
Example
from decimal import Decimal
# High precision division
numerator = Decimal('10.00')
denominator = Decimal('4.00')
result = numerator / denominator
print(result) # Output: 2.5Using Decimal, you can ensure that your division calculations are accurate to a high degree of precision, which is crucial for financial applications.
Here is the output you can see in the screenshot below:

5. Handling ZeroDivisionError
Dividing by zero is a common error that can crash your program. Python raises a ZeroDivisionError when this occurs. You can handle this using a try-except block.
Example
# Handling division by zero
numerator = 10
denominator = 0
try:
result = numerator / denominator
except ZeroDivisionError:
result = None
print("Cannot divide by zero")
print(result) # Output: NoneIn this example, attempting to divide by zero is caught by the except block, preventing the program from crashing.
Check out How to Increment a Variable in Python?
6. Divide a Variable in Python – Real-World Example
Now, let me show you a real-time example of how to divide a variable in Python.
Let’s consider a real-world example relevant to a U.S. audience: calculating the average gas price. Suppose you have the total amount spent on gas and the total gallons purchased; you can use division to find the average price per gallon.
Example
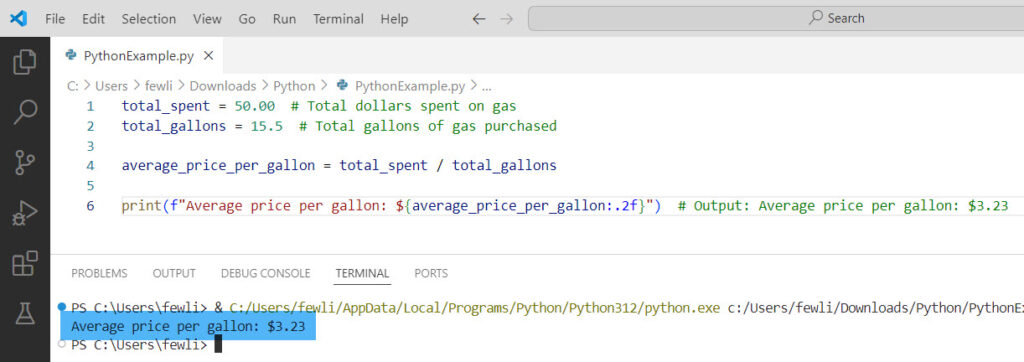
total_spent = 50.00 # Total dollars spent on gas
total_gallons = 15.5 # Total gallons of gas purchased
average_price_per_gallon = total_spent / total_gallons
print(f"Average price per gallon: ${average_price_per_gallon:.2f}") # Output: Average price per gallon: $3.23In this example, dividing the total amount spent by the total gallons purchased gives you the average price per gallon of gas.
You can see the exact output in the screenshot below:
Conclusion
I hope you know how to divide a variable in Python. I explained different methods and gave real-time examples. Also, you know how to handle the ZeroDivisionError error in Python that comes while doing division in Python.
You may also like:

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…