As a Python developer, you should know the difference between = and ==. In this tutorial, I will explain the difference between the assignment operator (=) and the equality operator (==) in Python with examples.
The Assignment Operator (=)
The assignment operator (=) in Python is used to assign a value to a variable. It doesn’t compare values; instead, it takes the value on the right-hand side and assigns it to the variable on the left-hand side.
Here is an example.
Example:
# Assigning values to variables
city = "New York"
population = 8419000In this example, the string "New York" is assigned to the variable city, and the integer 8419000 is assigned to the variable population.
The Equality Operator (==)
The equality operator (==) in Python is used to compare two values. It checks whether the values on either side of the operator are equal and returns True if they are, and False otherwise.
Let me show you an example.
Example:
# Comparing values
city1 = "Los Angeles"
city2 = "San Francisco"
print(city1 == city2) # Output: FalseHere, city1 is assigned the value "Los Angeles" and city2 is assigned "San Francisco". The == operator checks if the values of city1 and city2 are the same. Since they are not, the expression evaluates to False.
Check out Difference Between Mutable And Immutable In Python With Examples
Difference Between = and == in Python
Here’s a summary of the differences between = and == in Python.
| Feature | = (Assignment Operator) | == (Equality Operator) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Assigns a value to a variable | Compares two values for equality |
| Usage | variable = value | value1 == value2 |
| Example | city = "New York" | city1 == city2 |
| Operation | Stores the value on the right into the variable on the left | Checks if the values on both sides are equal |
| Return Type | None | Boolean (True or False) |
| Common Pitfall | Using = in conditions (results in syntax error) | Misunderstanding that it compares values, not assigns |
| Syntax Error Example | if (a = 5): (Invalid syntax) | if (a == 5): (Valid syntax) |
| Practical Example | population = 8419000 | state_capitals["Texas"] == "Austin" |
This table highlights the key differences and usage scenarios for the assignment operator (=) and the equality operator (==) in Python.
Check out Difference Between / and // in Python Division
Example: = and == in Python
Now, let me show you a practical example to understand the difference between = and == in Python. Suppose we are developing a simple program to check if a given city is the capital of a specific state.
Here is the complete code.
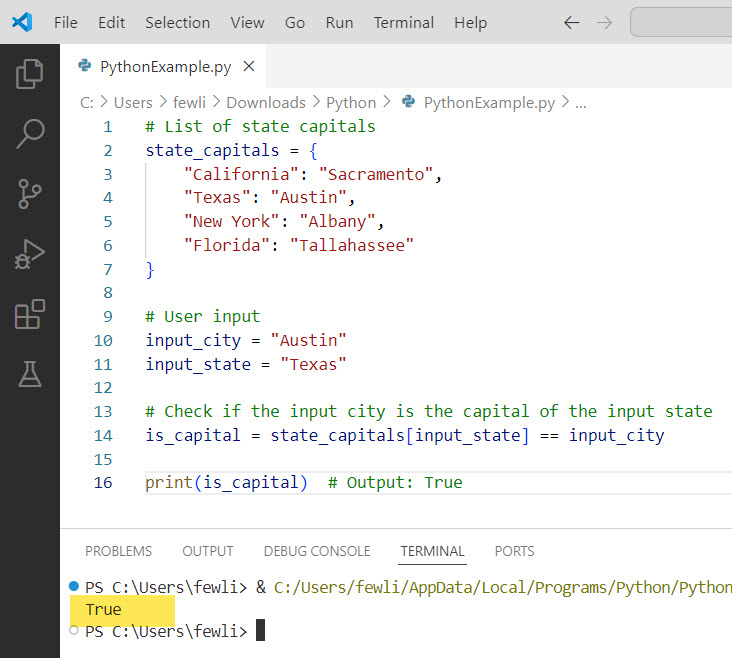
# List of state capitals
state_capitals = {
"California": "Sacramento",
"Texas": "Austin",
"New York": "Albany",
"Florida": "Tallahassee"
}
# User input
input_city = "Austin"
input_state = "Texas"
# Check if the input city is the capital of the input state
is_capital = state_capitals[input_state] == input_city
print(is_capital) # Output: TrueIn this example, we have a dictionary state_capitals that maps states to their capitals. We then take user input for a city and a state and use the == operator to check if the input city matches the capital of the input state. The assignment operator (=) is used to assign values to input_city and input_state, as well as to assign the result of the comparison to is_capital.
I executed the above Python code, and you can see the output in the screenshot below:
Conclusion
In Python, the assignment operator assigns values to variables, while the equality operator compares values. In this tutorial, I explained the difference between = and == in Python with examples.
You may also like:
- Divide a Variable in Python
- Subtract from a Variable in Python
- Multiply a Variable in Python
- Increment a Variable in Python
- Python Functions vs Methods

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…