Recently, I was working in a Python program where I needed to check if a global variable is defined. Python provides various methods to check it. In this tutorial, I will show you different methods to check if a global variable is defined in Python, with examples and complete code.
To check if a global variable is defined in Python, you can use the globals() function, which returns a dictionary of the current global symbol table. Simply check if the variable name exists in this dictionary. For example, if 'variable_name' in globals(): will return True if variable_name is defined globally, allowing you to handle it accordingly in your code.
Check if a Global Variable is Defined in Python
In Python, a global variable is a variable that is defined outside of any function and can be accessed from any part of the code. For example:
# Global variable
greeting = "Hello, USA!"
def print_greeting():
print(greeting)
print_greeting() # Output: Hello, USA!In this example, greeting is a global variable that can be accessed inside the print_greeting function.
Why Check if a Global Variable is Defined?
There are scenarios where you might need to check if a global variable is defined before using it. For instance, if you are developing a web application that relies on configuration settings stored in global variables, you need to ensure these variables are defined to avoid runtime errors.
Now, let me show you different methods to check if a global variable is defined with complete code and examples.
1. Using the globals() Function
The globals() function returns a dictionary representing the current global symbol table. You can use this dictionary to check if a variable is defined.
Here is an example.
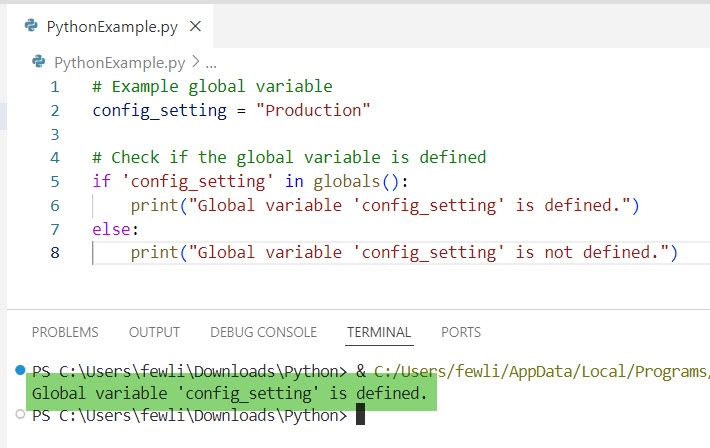
# Example global variable
config_setting = "Production"
# Check if the global variable is defined
if 'config_setting' in globals():
print("Global variable 'config_setting' is defined.")
else:
print("Global variable 'config_setting' is not defined.")In this example, the globals() function is used to check if config_setting is defined. If it is, the message “Global variable ‘config_setting’ is defined.” is printed.
I executed the above Python code, and you can see the output in the screenshot below:
Read How to Use Global Variables in Python Classes?
2. Using a Try-Except Block
Let me show you another method: Try-Except block.
You can use a try-except block to catch a NameError if the variable is not defined. The same applies to a global variable.
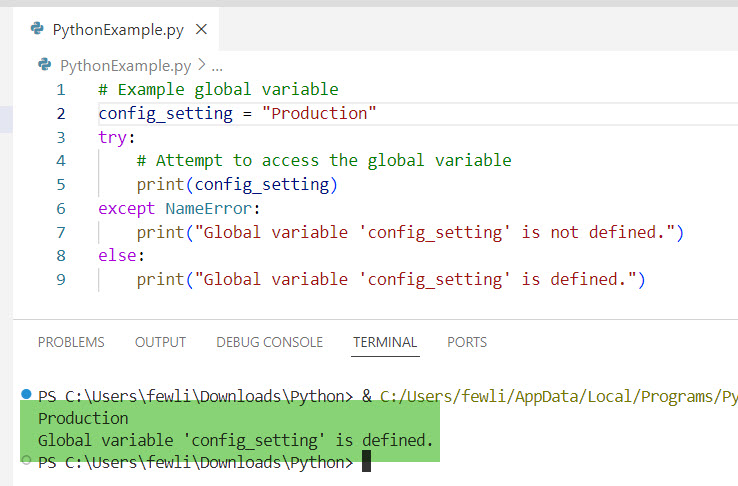
# Example global variableconfig_setting = "Production"
try:
# Attempt to access the global variable
print(config_setting)
except NameError:
print("Global variable 'config_setting' is not defined.")
else:
print("Global variable 'config_setting' is defined.")In this example, if config_setting is not defined, a NameError is caught, and the message “Global variable ‘config_setting’ is not defined.” is printed.
Here is the output you can see in the screenshot below:
Check out How to Check if a Variable is Global in Python?
3. Using the vars() Function
The vars() function returns the __dict__ attribute of a module, class, instance, or any other object. When called without arguments, it acts like globals(). This way, we can also check if a global variable is defined in Python.
Here is an example.
# Example global variable
api_key = "12345-ABCDE"
# Check if the global variable is defined
if 'api_key' in vars():
print("Global variable 'api_key' is defined.")
else:
print("Global variable 'api_key' is not defined.")This method works similarly to the globals() function and is useful when you want to use a more generic function.
You can see the output after I executed the above Python code using VS code in the screenshot below:

Practical Example: Web Application Configuration
Let’s consider a practical example where you are developing a web application for a local business in New York. The application uses global variables for configuration settings.
# Configuration settings
database_url = "localhost:5432"
api_key = "NYC-67890"
def connect_to_database():
if 'database_url' in globals():
print(f"Connecting to database at {database_url}")
else:
print("Database URL is not defined.")
def use_api():
if 'api_key' in globals():
print(f"Using API key: {api_key}")
else:
print("API key is not defined.")
connect_to_database() # Output: Connecting to database at localhost:5432
use_api() # Output: Using API key: NYC-67890In this example, the connect_to_database and use_api functions check if the database_url and api_key global variables are defined before using them. This ensures that the application can handle missing configuration settings gracefully.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, I have explained how to check if a global variable is defined in Python programming using different methods, such as the globals() function, try-except blocks, and the vars() function. Let me know in the comments below if you have any questions.
You may also like the following tutorials:
- How to Check if a Global Variable is Initialized in Python?
- How to Check if a Variable is Null in Python?

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…