Are you wondering how to change the value of a variable in Python? Let me tell you everything about it. In this tutorial, I will show you different methods to change the value of a variable in Python with examples and complete code.
To change the value of a variable in Python using the direct assignment method, simply use the = operator to reassign a new value to the existing variable. For example, if you initially set x = 5 and later want to change it, you can do so by writing x = 10.
Change the Value of a Variable in Python
Before changing the value of a Python variable, let us understand what a variable is.
A variable in Python is a symbolic name that refers to a value. Variables are created by assigning a value to a name using the = operator. For example:
x = 5In this example, x is a variable that holds the value 5.
Now, let me show you different methods to change the value of a variable in Python with examples.
1. Direct Assignment
The simplest way to change the value of a variable is through direct assignment in Python. You can reassign a new value to an existing variable using the = operator. Here is an example.
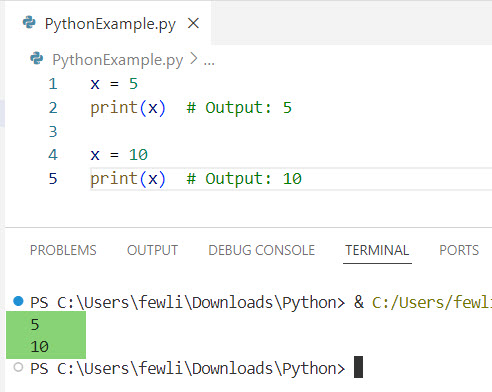
x = 5
print(x) # Output: 5
x = 10
print(x) # Output: 10In this example, the value of x is initially set to 5. Later, it is changed to 10 through direct assignment.
I executed the above Python code, and you can see the output in the screenshot below:
Check Declare a Variable Without Assigning a Value in Python
2. Using Arithmetic Operations
You can also change the value of a variable in Python by performing arithmetic operations and reassigning the result to the same variable.
Here is a simple example.
x = 5
print(x) # Output: 5
x = x + 3
print(x) # Output: 8
x -= 2
print(x) # Output: 6Here, the value of x is modified using the + and - operators. The shorthand operator -= is used to subtract 2 from x.
3. Using Functions
Variables in Python can be changed within functions. To modify a Python global variable inside a function, you need to use the global keyword.
x = 5
def change_value():
global x
x = 10
change_value()
print(x) # Output: 10In this example, the global keyword allows the function change_value to modify the global variable x.
Here is the output in the screenshot below:

Check out Access a Local Variable Outside a Function in Python Without Using global
4. Using Lists and Dictionaries
If you have a list or dictionary, you can change the value of elements within these data structures. Here are a few examples.
Lists
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
print(fruits) # Output: ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
fruits[1] = 'blueberry'
print(fruits) # Output: ['apple', 'blueberry', 'cherry']Dictionaries
person = {'name': 'John', 'age': 30}
print(person) # Output: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30}
person['age'] = 31
print(person) # Output: {'name': 'John', 'age': 31}In these examples, we modify elements within a list and a dictionary.
5. Using Environment Variables
In some cases, you might want to change the value of environment variables in your Python script. This can be done using the os module. Here is a simple example.
import os
os.environ['MY_VAR'] = 'initial_value'
print(os.environ['MY_VAR']) # Output: initial_value
os.environ['MY_VAR'] = 'new_value'
print(os.environ['MY_VAR']) # Output: new_value6. Using Classes and Objects
In object-oriented programming, you can change the value of instance variables within a class.
Here is how you can change the value of a variable in Python.
class Car:
def __init__(self, make, model):
self.make = make
self.model = model
my_car = Car('Ford', 'Mustang')
print(my_car.model) # Output: Mustang
my_car.model = 'F-150'
print(my_car.model) # Output: F-150In this example, we change the value of the model attribute of the my_car object.
Check out How to Use Global Variables in Python Classes?
Change the Value of a Variable in Python Example: Updating a Price List
Now, let me show you a real example of how to change the value of a variable in Python.
Suppose you want to update a price list for a grocery store.
prices = {
'apple': 1.5,
'banana': 0.75,
'milk': 3.0
}
print(prices) # Output: {'apple': 1.5, 'banana': 0.75, 'milk': 3.0}
# Updating the price of milk
prices['milk'] = 3.25
print(prices) # Output: {'apple': 1.5, 'banana': 0.75, 'milk': 3.25}
# Adding a new item
prices['bread'] = 2.5
print(prices) # Output: {'apple': 1.5, 'banana': 0.75, 'milk': 3.25, 'bread': 2.5}In this example, we update the price of milk and add a new item, bread, to the price list. Here is the output in the screenshot below:

Conclusion
In this tutorial, I have explained how to change the value of a variable in Python with examples using different methods. I hope the real example also helps you learn how to change the value of a variable in Python.
You may like the following tutorials:
- How to Check if a Global Variable is Initialized in Python?
- Check Type of Variable Is String in Python
- How to Check the Type of a Variable in Python?
- How to Check if a Variable Contains an Integer in Python?

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…