In Python programming, we use the main function. In this tutorial, I will show you how to call the main function in Python, its syntax, and a few examples.
To call the main function in Python, you first define the function using def main():, followed by your desired code inside this function. To ensure the main function is executed when the script is run directly, include the conditional statement if __name__ == "__main__": and call main() within it. This structure ensures that the main function is only executed when the script is run as the main program, not when it is imported as a module.
What is the Main Function in Python?
In Python, the main function serves as the entry point of a script. It is similar to the main function in other programming languages like C or Java. The main function is not a built-in function in Python but a convention used to indicate where the program should start executing.
Why Use the Main Function?
Using a main function in your Python script has several advantages:
- Improved Readability: It helps in organizing your code better.
- Reusability: You can reuse the functions defined in the script by importing them into other scripts without executing the main code block.
- Testing and Debugging: It makes testing and debugging easier since you can control the execution flow.
Syntax of the Main Function
The syntax to define and call the main function in Python is straightforward. Here’s a basic example:
def main():
print("Hello, World!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()In this example:
def main():defines the main function.if __name__ == "__main__":checks if the script is being run directly or being imported as a module. If the script is run directly, it calls themain()function.
Check out Python Functions vs Methods
Call the Main Function in Python
Now let me show how to call the main function in Python with different scenarios and examples.
Scenario 1: Basic Script Execution
When you run the script directly, the main function will be executed. Here’s a simple example:
def main():
print("This is the main function.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()When you run this script, it will print:
This is the main function.Here is the exact output you can see in the screenshot below:

Scenario 2: Importing the Script as a Module
If you import the script containing the main function into another script, the main function will not execute unless explicitly called. For example, consider the script above saved as script.py. Now, create another script:
import script
script.main() # Explicitly calling the main functionIn this case, the main function from script.py will be called and executed.
Check out Python Function Naming Conventions
Scenario 3: Passing Arguments to the Main Function
You can also pass arguments to the main function in Python. This is particularly useful for command-line applications. Here’s an example:
import sys
def main(args):
print(f"Arguments passed: {args}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(sys.argv[1:])When you run this script with arguments, for example, python script.py arg1 arg2, it will print:
Arguments passed: ['arg1', 'arg2']You can see the exact output in the screenshot below:

Scenario 4: Using Main Function in Larger Projects
In larger projects, the main function can help in organizing the code better. Here’s an example of a more complex script:
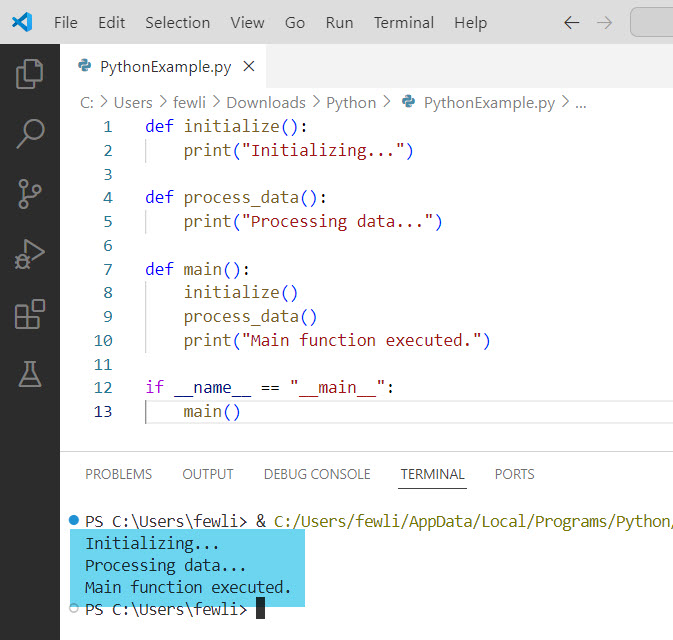
def initialize():
print("Initializing...")
def process_data():
print("Processing data...")
def main():
initialize()
process_data()
print("Main function executed.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()This structure helps separate different parts of the code, making it more maintainable and readable.
Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, I have explained how to call the main function in Python with different examples.
You may also like:

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…