In the Python New York user group, someone wanted to know about the ord function in Python. I thought I would write a complete tutorial on this. In this tutorial, I will explain everything about the ord() function in Python with examples.
The ord function in Python is a built-in function that returns the Unicode code point of a given character. Its syntax is simple: ord(character), where character is a single-character string. For example, ord('A') returns 65, the Unicode code point for ‘A’. This function is particularly useful for tasks involving data encoding, text processing, and cryptography.
What is the ord Function in Python?
The ord function in Python is a built-in function that returns the Unicode code point for a given character. This function is particularly useful when you need to convert a character into its corresponding integer representation.
Syntax of the ord Function
The syntax for the ord function is:
ord(character)character: A string of a single character whose Unicode code point you want to find.
How Does the ord Function in Python Work?
The ord function takes a single character as an argument and returns an integer representing the Unicode code point of that character. This is useful in various scenarios, such as encoding and decoding data, or when working with character-based data processing.
Check out POP() Function in Python
Examples of ord() function in Python
Now, let me show you some examples of how the ord function works in Python.
Example 1: Basic Usage
In this example, we’ll convert the character ‘A’ to its Unicode code point.
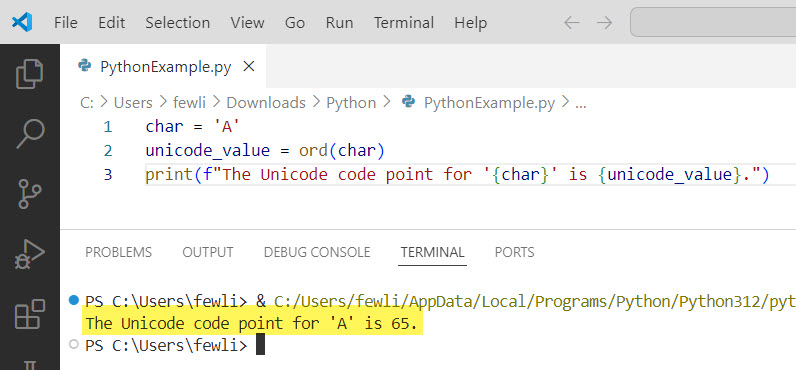
char = 'A'
unicode_value = ord(char)
print(f"The Unicode code point for '{char}' is {unicode_value}.")Output:
The Unicode code point for 'A' is 65.I executed the above Python code using VS code, and you can see the exact output in the screenshot below:
Example 2: Using ord with Special Characters
Let’s see how the ord function handles special characters like ‘@’.
char = '@'
unicode_value = ord(char)
print(f"The Unicode code point for '{char}' is {unicode_value}.")Output:
The Unicode code point for '@' is 64.Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:

Check out Range Function in Python
Example 3: Convert Lowercase Letters
Here, we’ll convert a lowercase letter ‘z’ to its Unicode code point.
char = 'z'
unicode_value = ord(char)
print(f"The Unicode code point for '{char}' is {unicode_value}.")Output:
The Unicode code point for 'z' is 122.Example 4: Using ord with Numeric Characters
The ord function can also be used with numeric characters.
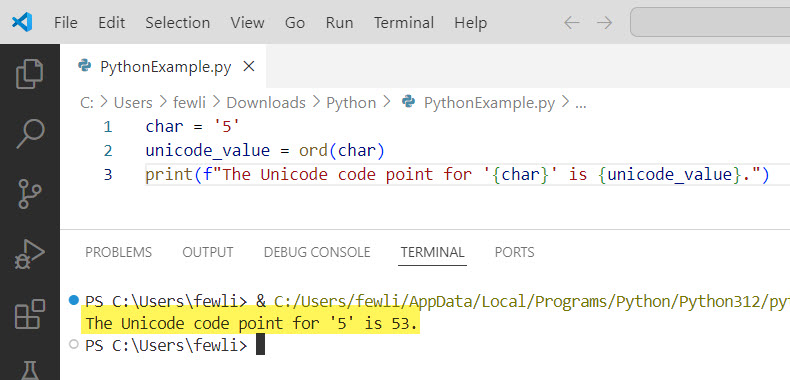
char = '5'
unicode_value = ord(char)
print(f"The Unicode code point for '{char}' is {unicode_value}.")Output:
The Unicode code point for '5' is 53.Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:
Conclusion
The ord function in Python is useful for converting characters to their Unicode code points. I explained how to use the ord() function in Python in this tutorial with some examples.
You may also like:

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…