Do you want to know how to Increment a variable in Python? In this tutorial, I will show you various ways to increment a variable in Python using clear examples and practical scenarios. So, it will be helpful to you.
To increment a variable in Python, the most common and efficient method is using the addition assignment operator (+=). This operator adds the specified value to the variable and reassigns the result back to it. For example, if you have a variable counter initialized to 0, you can increment it by 1 using counter += 1, resulting in counter being 1.
1. Using the Addition Assignment Operator (+=)
The best way to increment a variable in Python is by using the addition assignment operator (+=). This operator adds the value on the right to the variable on the left and assigns the result to the variable. Let me show you an example also.
Example:
# Incrementing by 1
counter = 0
counter += 1
print(counter) # Output: 1
# Incrementing by any other number
counter += 5
print(counter) # Output: 6In this example, we start with counter set to 0. The statement counter += 1 increments counter by 1, making it 1. We then increment it by 5, resulting in 6.
I executed the above Python code using VS code, and you can see the output in the screenshot below:
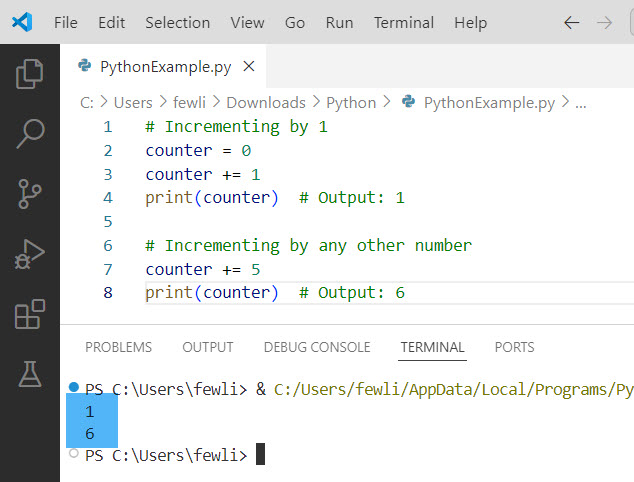
Check out How to Multiply a Variable in Python?
2. Using the + Operator
In Python, you can also increment a variable using the + operator, though this method is less common because it requires explicitly assigning the result to the variable. Here is an example.
Example:
# Incrementing by 1
counter = 0
counter = counter + 1
print(counter) # Output: 1
# Incrementing by any other number
counter = counter + 5
print(counter) # Output: 6This method achieves the same result as the += operator but is more verbose.
You can also see the exact output in the screenshot below:
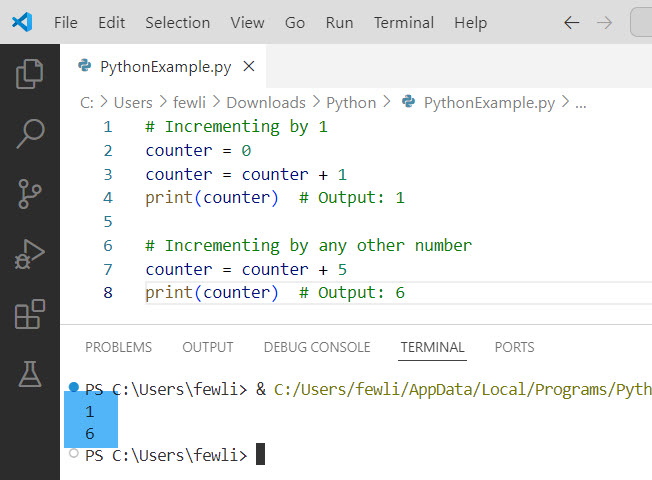
Check out How to Subtract from a Variable in Python?
3. Using a Function
You might want to encapsulate the increment operation within a function for more complex scenarios. This can be useful for maintaining clean and reusable code. Here is the complete Python code and example.
Example:
def increment(value, increment_by=1):
return value + increment_by
counter = 0
counter = increment(counter)
print(counter) # Output: 1
counter = increment(counter, 5)
print(counter) # Output: 6In this example, the increment function takes two arguments: the value to be incremented and the increment value (defaulting to 1). Here is the exact output in the screenshot below:

Read Divide a Variable in Python
4. Using a Loop
Python’s simple syntax makes incrementing a variable within a loop easy. Let’s understand with an example.
Example:
counter = 0
for i in range(10):
counter += 1
print(counter) # Output: 10Here, we increment counter by 1 for each iteration of the loop, resulting in a final value of 10. Here is the exact output.
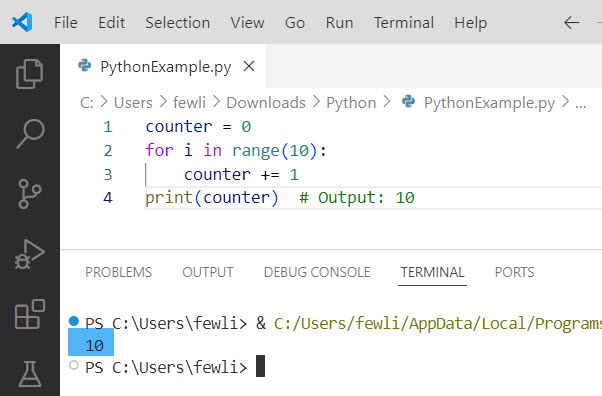
Python increment by 1
To increment a variable by 1 in Python, you can use the addition assignment operator (+=). This operator adds the specified value to the variable and reassigns the result back to it.
Let me show you an example.
counter = 0 # Initialize the variable
counter += 1 # Increment by 1
print(counter) # Output: 1In this example, counter starts at 0. The statement counter += 1 increments counter by 1, resulting in counter being 1.
You can see the output in the screenshot below:
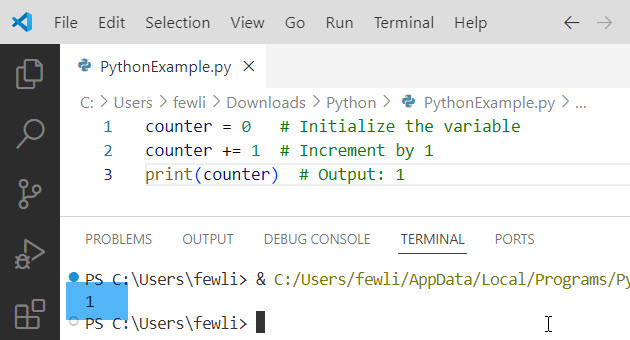
Practical Example: Counting Items in a Shopping Cart
Let’s consider a practical example for understanding increment a variable in python: counting items in a shopping cart. Suppose you’re developing an e-commerce application and need to keep track of the number of items in a user’s cart.
Example:
# Initial number of items in the cart
cart_items = 0
# User adds items to the cart
cart_items += 3 # User adds 3 items
print(cart_items) # Output: 3
cart_items += 2 # User adds 2 more items
print(cart_items) # Output: 5In this example, we start with an empty cart (cart_items = 0). As the user adds items, we increment the cart_items variable accordingly.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, I have explained how to increment a variable in Python using different methods, such as using the += operator, the + operator, a function, or within a loop, etc. I hope you understand it from the above real-time examples.
You may also like:
- How to Print a New Line After a Variable in Python?
- Difference Between / and // in Python Division
- How to Divide a Variable in Python?

I’m Michelle Gallagher, a Senior Python Developer at Lumenalta based in New York, United States. I have over nine years of experience in the field of Python development, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. My expertise lies in Python and its extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Throughout my career, I’ve had the pleasure of working on a variety of projects that have leveraged my skills in Python and machine learning. Read more…